CIVIL
LABORATORY
in particular...
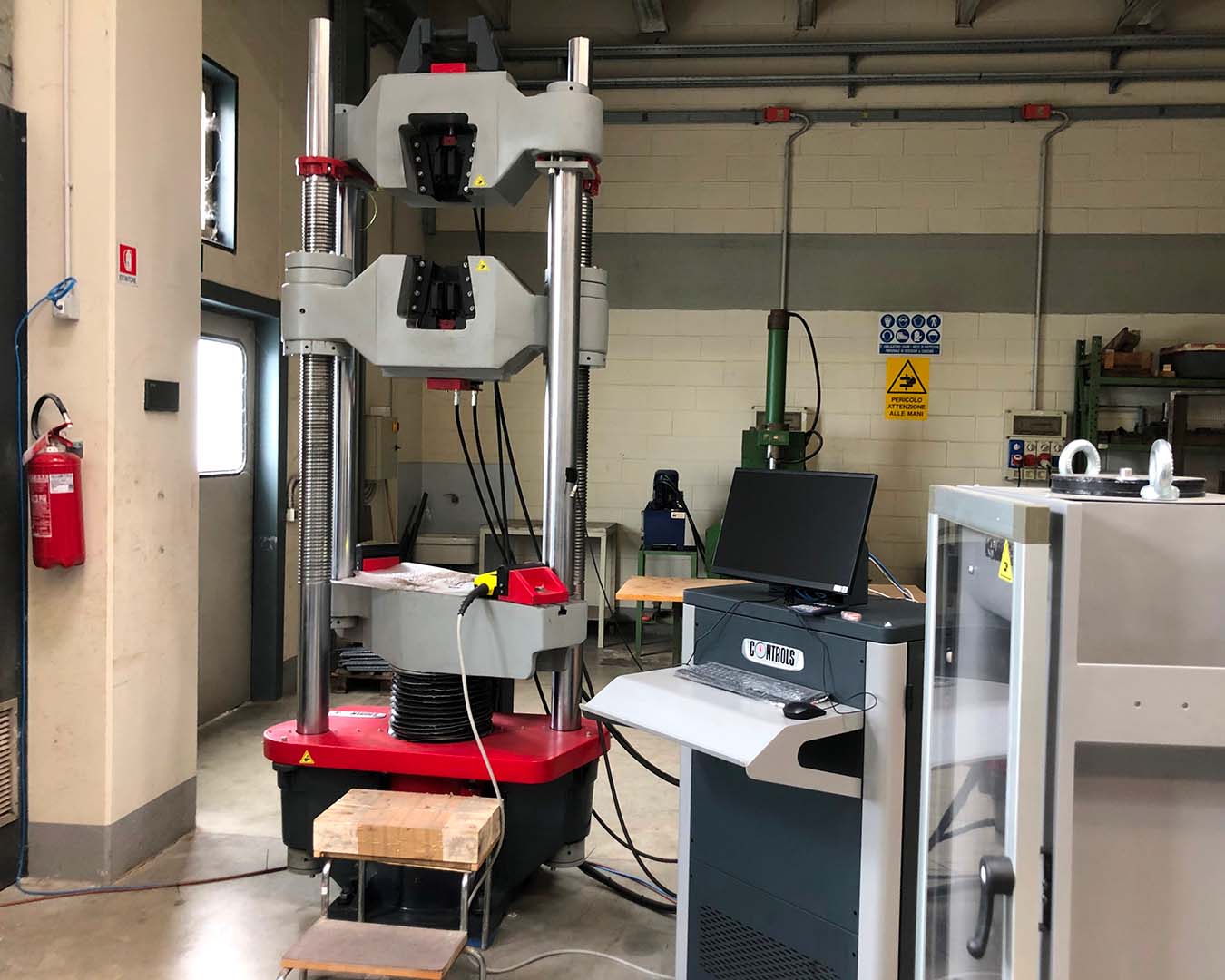
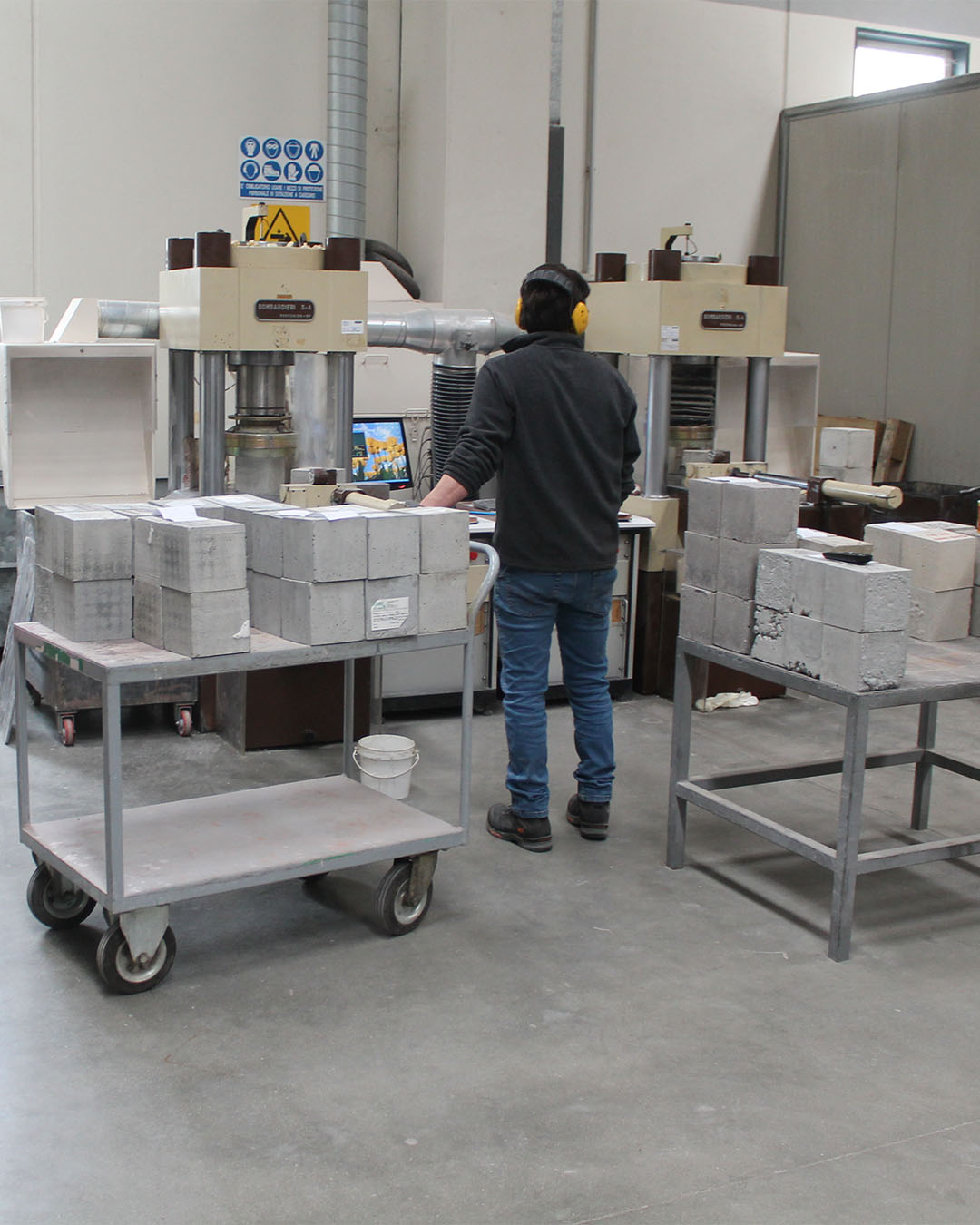
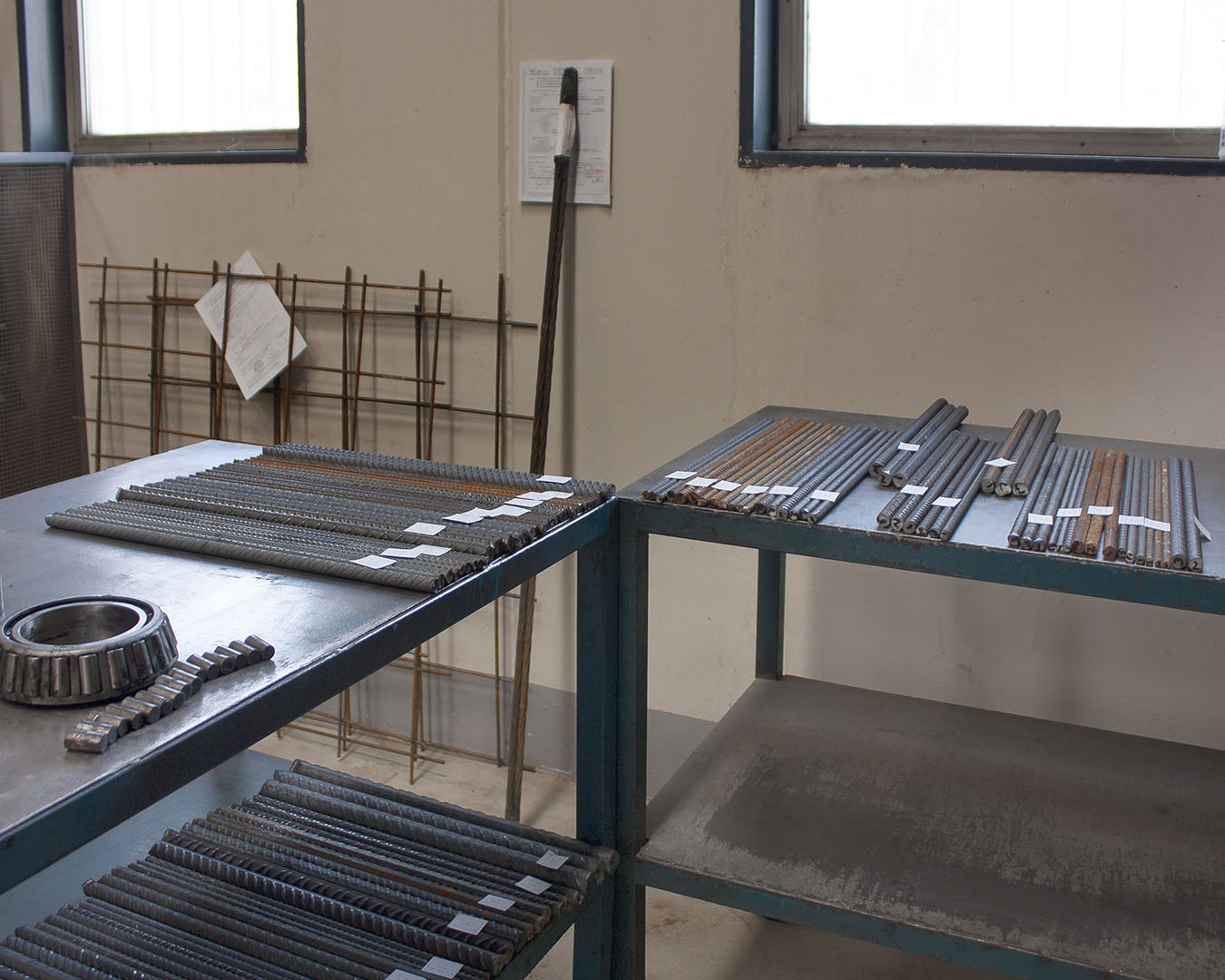
The Material Testing Laboratory of P&P LMC srl is an Official Laboratory pursuant to Law 1086/71 art. 20 and Presidential Decree 380/01 art. 59, authorized by the Higher Council of Public Works to perform tests on construction materials (concrete cubes, reinforcing bars, carpentry, etc.) for the issue of the Official Certificates necessary for the testing of structures pursuant to the Presidential Decree 380/01 art. 67.
According to the Technical Standards for Construction referred to in the D.M. 17.01.2018, also the taking of samples from the structures (core drilling and extraction of bars) and the relative compression and traction tests, for the purpose of evaluating existing buildings, must be carried out by an Official Laboratory.
The Materials Testing Laboratory carries out the necessary tests for the CE marking of construction materials (CPR regulation 305/11), in accordance with the relevant harmonized product standards.
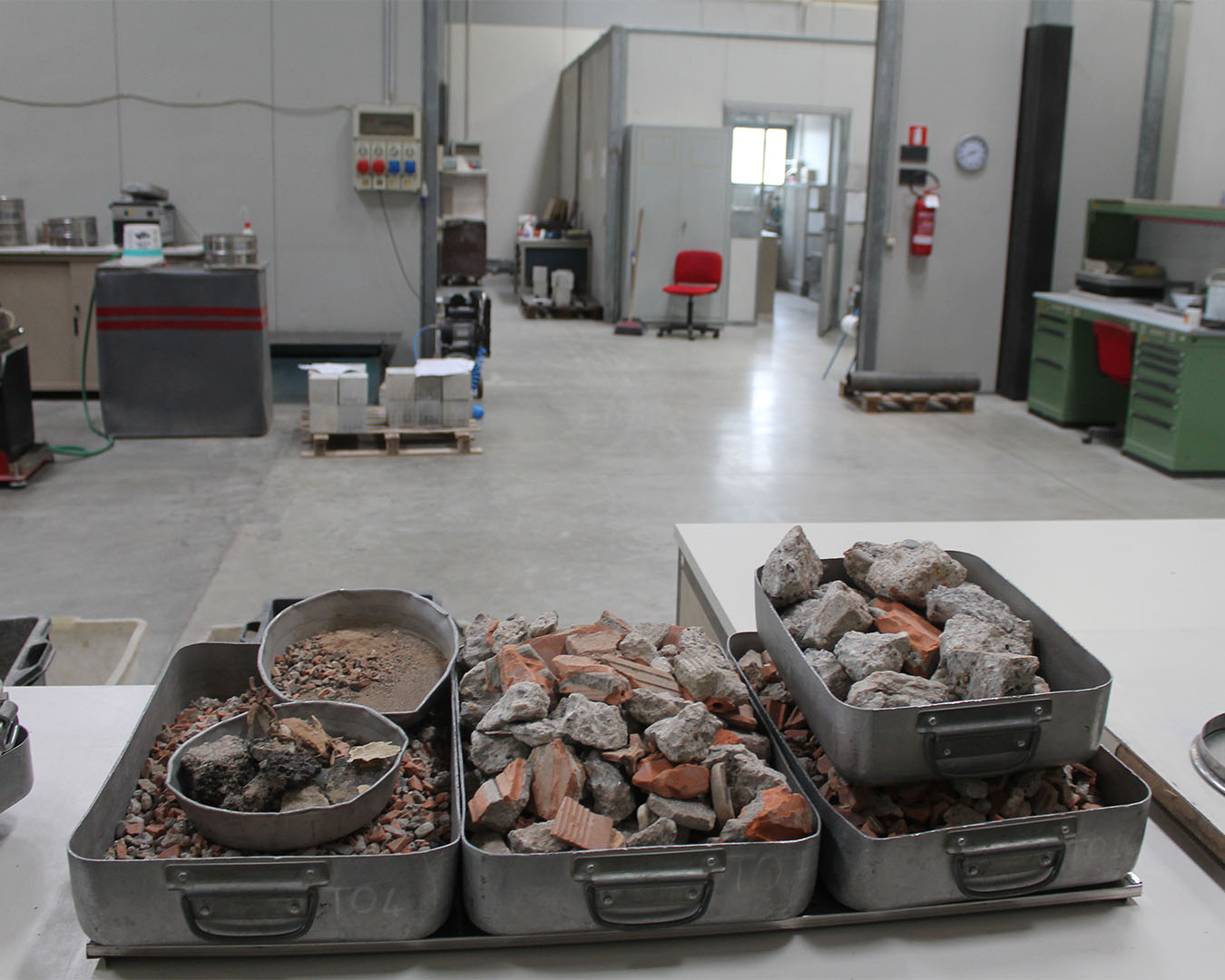
The main tests for the characterization of the aggregates for the purposes of CE marking are carried out in accordance with the provisions of the standards: UNI EN 12620, UNI EN 13043 and UNI EN 13242.
In addition, the P&P LMC Srl Laboratory performs the determination of the performance characteristics of the recycled aggregates (MPS) pursuant to Annex C of circular no. 5205 of 15.07.2005
DOWNLOAD THE FORMS FOR REQUESTING THE MATERIAL TEST LABORATORY
- Request for Material Tests: concrete, reinforcing bars and electro-welded mesh
- Request for material tests: structural steel
- Request for material tests: concrete cores
- Load Test Request: on plate, bearing capacity, on poles
- Load Tests Request: on screws
- Request for tests: bituminous conglomerates.
OUR LABORATORIES
CHEMICAL LABORATORY
The main laboratory activities are: sem, earth and rocks, waste, water analysis, emissions and work environments, airborne sampling.
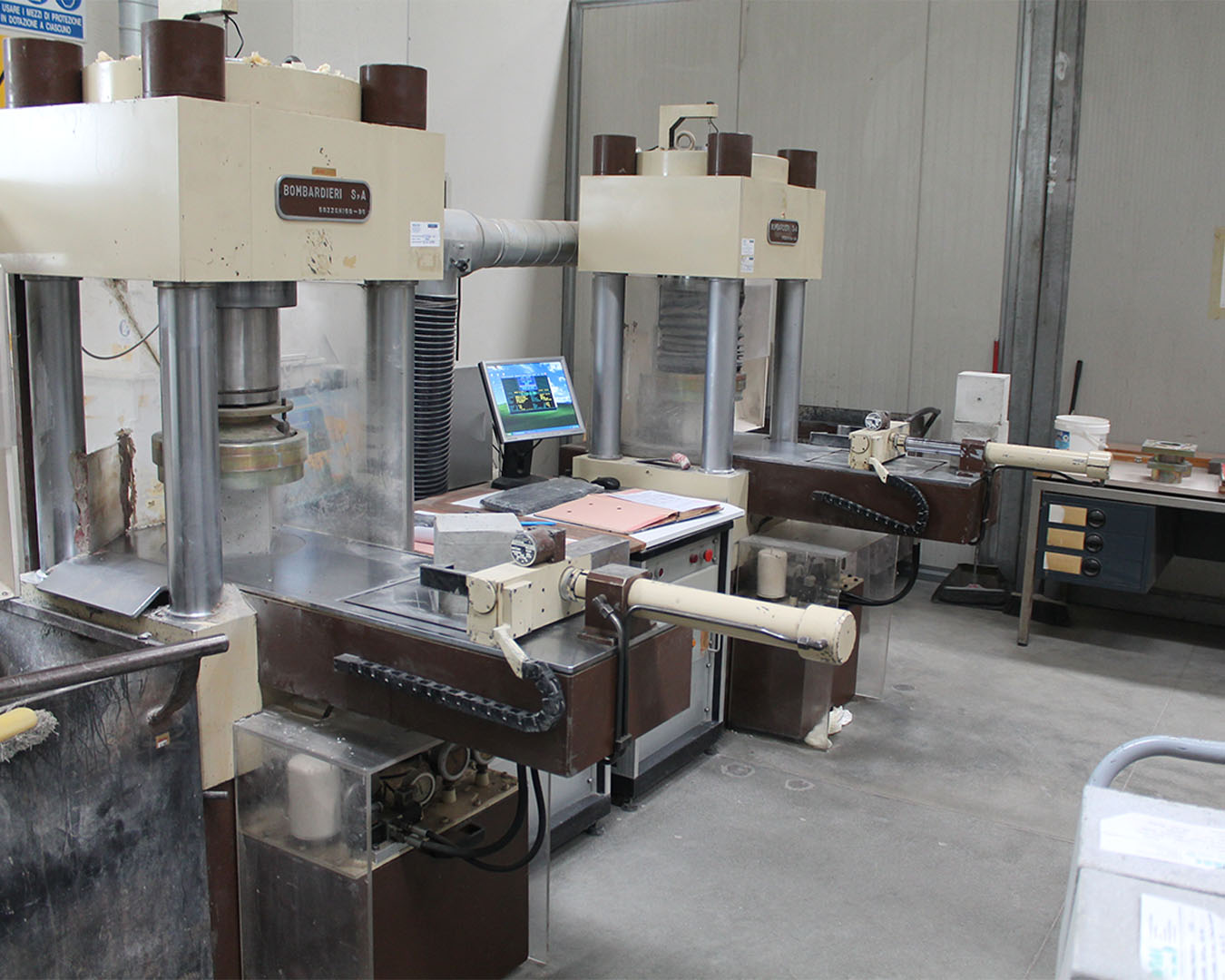
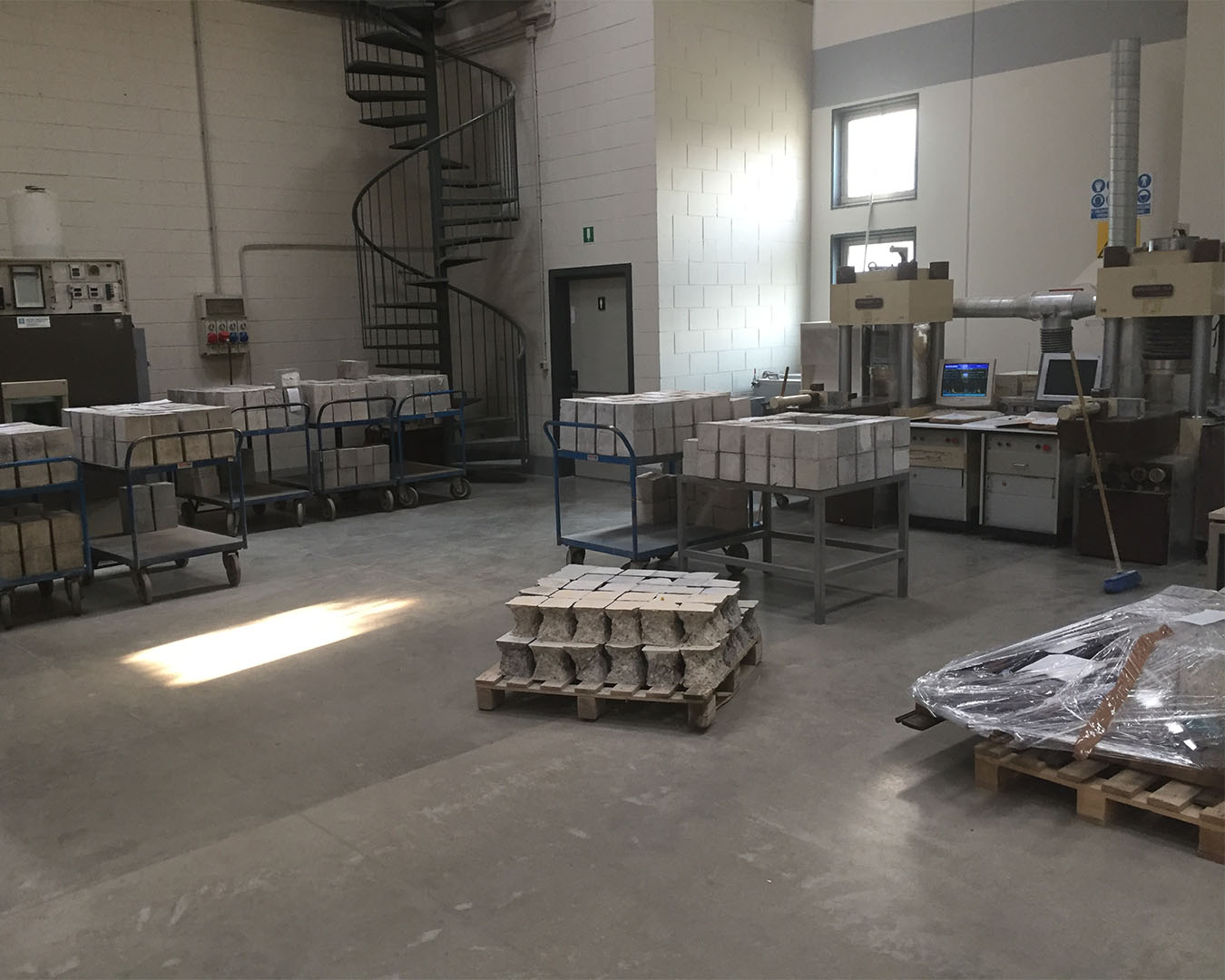
MECHANICAL TESTS LABORATORY
The mechanical testing laboratory carries out activities aimed at the verification, control, approval and qualification of materials.
EXISTING BUILDINGS LABORATORY
The existing buildings laboratory supports the professional in drawing up the investigation plan, carrying out tests compliant with regulations and carrying out the restoration of the test points.
INSTRUMENT CALIBRATION
P&P provides a calibration and certification service for mechanical, electromechanical, electronic, chemical measuring instruments.
The activities of the Laboratory are aimed at:
- Companies
- Manufacturers of building materials and products
- Building planners and construction supervisors
- Sector technicians and consultants
- Certification entities
An integral service of support and assistance is offered in the fields of civil and infrastructural engineering, thanks to the execution of a wide range of tests, both in the laboratory and in the field, which mainly concern: concrete, reinforcement for reinforced concrete, strands and wires. for reinforced concrete, electro-welded meshes and lattices, structural steel, bricks and elements for masonry, aggregates, bituminous conglomerates, cements and mortars, additives and mixing water, additives (fly ash, silica fume, etc.), natural stone, concrete blocks for flooring, diagnostics of cultural heritage, coring and on-site checks, plate and lift tests, on-site density, geotechnical characterizations.
We also perform petrographic investigations with observation under the stereomicroscope and polarizing optical microscope and thermogravimetric analyzes of mortars and concrete.
TGA TESTS AND PETROGRAPHIC ANALYSIS
Petrography allows to know the mineralogical / petrographic composition of mortars and plasters.
Thermogravimetric analyzes are aimed at analyzing the hydraulic compounds present in the binder fraction.
Thermogravimetric analyzes (TGA) and optical microscope observations of polished sections (thin sections or polished sections) have the objective of investigating concretes, mortars and plasters, of historic buildings and new constructions. By combining the two methods it is possible to recognize events such as chemical and structural changes, as well as the observation of exothermic and endothermic reactions that develop in the sample. It is therefore possible to obtain a reliable definition of the composition of the cement conglomerates analysed: lime mortar, mortar of lime and cement or cement only, of silicate or carbonate composition, indicative content of the primer and binder mass.
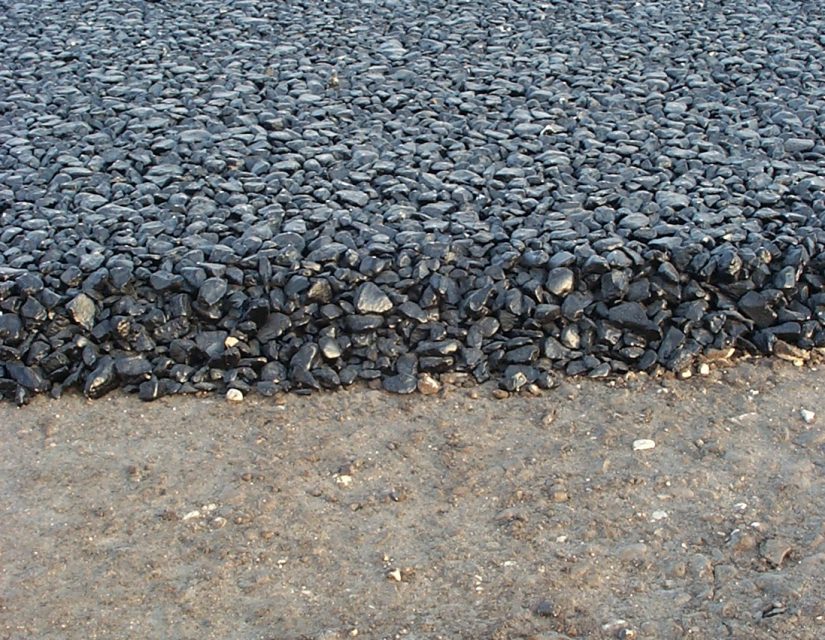
TESTS ON BITUMEN CONGLOMERATES
PROVE CONGLOMERATI BITUMINOSI
The Laboratory is equipped with instruments for qualification and control during the laying phase on various bituminous conglomerates, with determination of the binder content and granulometry of the extracted aggregate. P&P also takes care of the checks after the installation by means of on-site coring of the conglomerate and subsequent laboratory determinations on the extracted specimens.
In addition, P&P offers the test specimen packaging service in the laboratory with a turntable press or Marshall compactor, on which to perform the necessary characterizations:
- Compactability;
- Density;
- Void content (void index);
- Marshall test;
- Indirect tensile strength;
- Sensitivity to water;
FRP AND FRCM TESTING
PROVE CONGLOMERATI BITUMINOSI
FRP (Fiber Reinforced Polymers) - and FRCM (Fabric Reinforced Cementitious Matrix) testing plays a crucial role in assessing the strength and durability of reinforced or repaired structures. These advanced materials are widely used in civil engineering to improve mechanical performance and extend the lifespan of existing buildings and infrastructures.
FRP (Fiber Reinforced Polymers)
FRP consists of high-strength fibers (such as carbon, glass, or aramid) embedded in a polymer matrix. They are used to reinforce structural elements such as beams, columns, and walls. The key advantages of FRP are:
- Lightweight:they reduce the additional load on the structure.
- High tensile strength:Carbon fibers, for example, have a much higher strength-to-weight ratio than steel
- Corrosion resistance: unlike steel, FRP does not corrode, making them ideal for aggressive environments.
Testing on FRP materials includes:
- Tensile testing to determine tensile strength and elastic modulus.
- Adhesion testing to evaluate the bond quality between FRP reinforcement and the substrate (concrete, masonry, etc.).
FRCM (Fabric Reinforced Cementitious Matrix)
FRCM is an innovative system that combines fiber meshes (carbon, glass, PBO) with a cementitious matrix. Compared to FRP, it offers greater compatibility with traditional materials (such as historical masonry and concrete) and better resistance to high temperatures.
The advantages of FRCM include:
- Compatibility with mineral substrates: the FRCM system is more similar to traditional construction materials like concrete and masonry.
- Fire resistance:the cementitious matrix performs better in high-heat environments.
- Ease of application: it can be used on irregular surfaces or historic structures without altering their appearance.
FRCM testing includes:
- Compression testing to determine the compressive strength.
- Flexural and shear testing to evaluate performance under different stresses.
- Adhesion and durability testing to assess resistance to aging and environmental load cycles.
The civil laboratory of P&P LMC conducts a wide range of tests to verify the mechanical properties and durability of these materials, contributing to improving the safety and reliability of reinforced structures.
Reference Standards for FRP and FRCM Testing
The use of FRP and FRCM for structural reinforcement is governed by specific standards to ensure proper testing and safe application of the materials. Below are the main reference standards:
For FRP (Fiber Reinforced Polymers):
- CNR-DT 200 R1/2013 – "Guidelines for the design, execution, and control of static consolidation interventions using fiber-reinforced composites" (Italian standard).
- EN 13706 – European standards for fiber-reinforced composite materials.
- ISO 10406-1 – "Fiber-reinforced polymer (FRP) reinforcement of concrete".
For FRCM (Fabric Reinforced Cementitious Matrix):
- CNR-DT 215/2018 Guidelines for the design, execution, and testing of static consolidation interventions using fiber-reinforced composites with inorganic matrix".
- EN 1504-4 – “Products and systems for the protection and repair of concrete structures”
ACTIVITIES OF THE MATERIAL TEST LABORATORY
| TESTS ON METALLIC MATERIALS | TESTS ON METALLIC MATERIALS |
| Title Test | Number Standard |
| Impact test with Charpy pendulum | UNI EN ISO 148-1 |
| Traction of metallic materials at room temperature | UNI EN ISO 6892-1 |
| Tensile test on bars, rolls and wires for reinforced concrete | UNI EN ISO 15630-1 |
| Tensile test on nets and pylons for reinforced concrete | UNI EN ISO 15630-2 |
| Tensile test on strands and wires for reinforced concrete | UNI EN ISO 15630-3 |
| Bending test | UNI EN ISO 7438 |
| Steel wires - Test methods (alternating bending) | UNI EN 10218 |
| TESTS ON HARDENED CONCRETE | |
| Title Test | Number Standard |
| Packaging and curing of the specimens | UNI EN 12390-2 |
| Compressive strength of the specimens | UNI EN 12390-3 |
| Flexural strength of specimens | UNI EN 12390-5 |
| Indirect traction (Brazilian) | UNI EN 12390-6 |
| Density of hardened concrete | UNI EN 12390-7 |
| Penetration of water under pressure | UNI EN 12390-8 |
| Freeze-thaw, flaking | UNI CEN/TS 12390-9 |
| Modulus of elasticity in concrete | UNI EN 12390-13 |
| Shrinkage of concrete | UNI EN 12390-16 |
| Concrete cores - Picking and compression | UNI EN 12504-1 |
| Hammer index | UNI EN 12504-2 |
| TESTS ON FRESH CONCRETE | |
| Title Test | Number Standard |
| Determination of the water content | UNI 11201 |
| Sampling | UNI EN 12350-1 |
| Lowering to the cone | UNI EN 12350-2 |
| Test Vebè | UNI EN 12350-3 |
| Compactability index | UNI EN 12350-4 |
| Table spreading with shocks | UNI EN 12350-5 |
| Density | UNI EN 12350-6 |
| Air content | UNI EN 12350-7 |
| SCC: spreading and spreading time | UNI EN 12350-8 |
| SCC: V funnel outflow time (V-funnell) | UNI EN 12350-9 |
| SCC: L-box sliding confined (L-box) | UNI EN 12350-10 |
| SCC: segregation by sieve | UNI EN 12350-11 |
| SCC: J-ring confined sliding | UNI EN 12350-12 |
| TESTS ON MASONRY ELEMENTS | |
| Title Test | Number Standard |
| Masonry elements - Compressive strength | UNI EN 772-1 |
| Masonry elements - Percentage of drilling | UNI EN 772-2 |
| Mechanical resistance | UNI EN 196-1 |
| Chemical analysis | UNI EN 196-2 |
| Setting times and stability | UNI EN 196-3 |
| Pozzolanicity test | UNI EN 196-5 |
| Fineness | UNI EN 196-6 |
| Chromium VI content | UNI EN 196-10 |
| Historical mortars - CO2 content | UNI 11140 |
| TESTS ON AGGREGATES AND EARTH | TESTS ON AGGREGATES AND EARTH |
| Title Test | Number Standard |
| Visual separation tratt. 8 mm (circ. 5205) | UNI EN 13285 |
| Earths and mixtures of unbound aggregates | UNI 11531-1 |
| Land identification and description | UNI EN ISO 14688-1 |
| Petrographic description | UNI EN 932-3 |
| Particle size analysis | UNI EN 933-1 |
| Flattening index | UNI EN 933-3 |
| Shape index | UNI EN 933-4 |
| Crushed surfaces | UNI EN 933-5 |
| Slip coefficient | UNI EN 933-6 |
| Contains of shells | UNI EN 933-7 |
| Equivalent in sand | UNI EN 933-8 |
| Methylene blue | UNI EN 933-9 |
| Constituents large aggregate recycled | UNI EN 933-11 |
| Micro-Deval | UNI EN 1097-1 |
| Los Angeles | UNI EN 1097-2 |
| Density in heap | UNI EN 1097-3 |
| Water content for drying | UNI EN 1097-5 |
| Density and absorption | UNI EN 1097-6 |
| Polishing value | UNI EN 1097-8 |
| Frost Thaw | UNI EN 1367-1 |
| Test with magnesium sulphate | UNI EN 1367-2 |
| Thermal shock | UNI EN 1367-5 |
| Chemical analysis: noun humica, chlorides, sulphates, etc. | UNI EN 1744-1 |
| Alkali-aggr reactivity assessment method | UNI 8520-22 |
| Alkali / Aggregate Reactivity - Expansion acc. mortar | UNI 11504 |
| TESTS ON BITUMINOUS CONGLOMERATES | |
| Title Test | Number Standard |
| Granulometry of the extracted aggregate | UNI EN 12697-2 |
| Maximum density of the specimens | UNI EN 12697-5 |
| Apparent density of the specimens | UNI EN 12697-6 |
| Determination of voids | UNI EN 12697-8 |
| Compactability | UNI EN 12697-10 |
| Bitumen aggregate affinity | UNI EN 12697-11 |
| Determination of sensitivity to water | UNI EN 12697-12 |
| Cantabro test (loss of particles from the specimen) | UNI EN 12697-17 |
| Indirect tensile strength of the specimens | UNI EN 12697-23 |
| Collecting cores from paving | UNI EN 12697-27 |
| Collection of loose bituminous conglomerate | UNI EN 12697-27 |
| Determination of size of specimens | UNI EN 12697-29 |
| Preparation of the specimen with impact compactor | UNI EN 12697-30 |
| Preparation of the specimen with a rotary press | UNI EN 12697-31 |
| Marshall test | UNI EN 12697-34 |
| Determination of thickness of paving layers | UNI EN 12697-36 |
| Binder content - Ignition method | UNI EN 12697-39 |